mebioda
Data science tools
UNIX/Linux operating systems: why do we care?
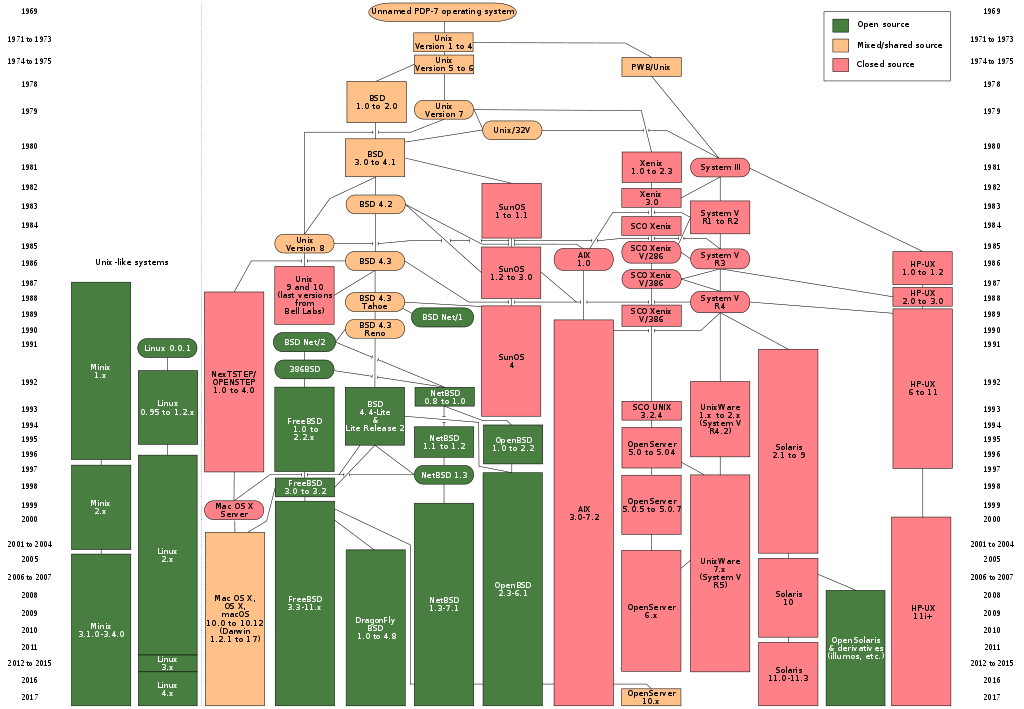
- Have better facilities for automation (shell scripting)
- A lot of scientific software is (only) written for them
- Linux is free, so analytical environments can be copied and instantiated in virtualization environments with few restrictions
UNIX file system conventions
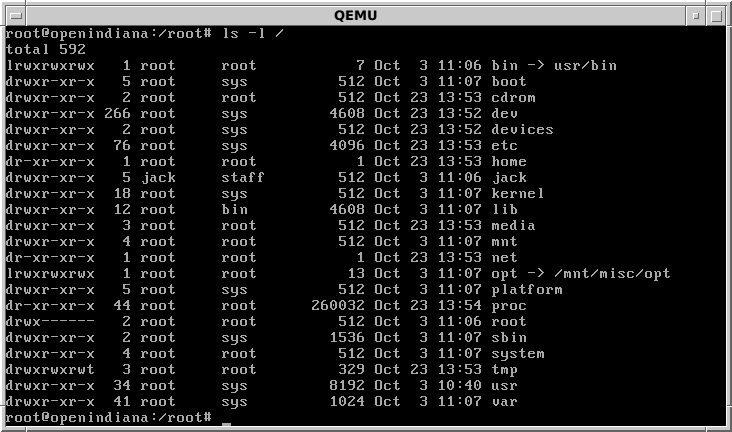
UNIX-like file systems:
- start at the root:
/ - are hierarchical trees navigated with paths:
- absolute paths start from the root, e.g.
/home/mebioda - relative paths go from one location to another, e.g.
../../tmp
- absolute paths start from the root, e.g.
- consider everything a “file”
- consider files simple byte arrays (and text)
- follow some organizational conventions
| Directory | Description |
|---|---|
/bin |
Single user binaries |
/dev |
Hardware devices |
/etc |
Configuration files |
/home |
User home dirs |
/lib |
Libraries |
/sbin |
System binaries |
/tmp |
Temporary files |
/usr |
Multi user utilities |
/var |
Variable files |
File access
- Access to files is granted at user and group level
- Files can be read (r), written (w) and/or executed (x)
- To read from or write to a file, a file handle is opened
- File extensions don’t matter
Commonly-used file operations
| Command | Function | Command | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
ls |
List files | mv |
Rename/move files |
cd |
Change directory | mkdir |
Make directory |
pwd |
Print working directory | rmdir |
Remove directory |
rm |
Remove files | chmod |
Change file mode |
cp |
Copy files | chown |
Change file owner |
# file listing
$ ls
# long (-l) listing of all (-a) files, sizes in (-h) human readable format:
$ ls -lah
# manual pages of ls
$ man ls
File modes
- Files can be readable, writable, and/or executable
- Files belong to users, who belong to a group but not to the others
chmod permission bits:
| bits | code | value | 2n |
|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | x | 1 | 20 |
| 010 | w | 2 | 21 |
| 100 | r | 4 | 22 |
Hence:
- rwx = 111 = 1+2+4 = 7
- rw = 110 = 2+4 = 6
- r = 100 = 4
# set text file rw for user, r for others:
$ chmod 644 file.txt
# set script rwx for user, rx for others:
$ chmod 755 script.sh
Commonly-used text operations
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
more |
Page through text |
head |
View first lines |
tail |
View last lines |
grep |
Search for pattern |
sed |
Search and replace |
sort |
Sort lines |
uniq |
Filter duplicate lines |
cut |
Cut columns from table |
paste |
Concatenate columns |
join |
Join matching columns |
cat |
Print file contents |
wc |
Word count |
awk |
Tabular data processing |
UNIX pipes
- UNIX programs by default write to STDOUT and read from STDIN
- The defaults can be re-directed with “> outfile” and “< infile”, respectively
-
The output from one program can be piped into the input from the next:
cat file | sort | uniq > sorted_no_dups
UNIX programming
- UNIX provides a standardized environment for developing applications (historically in C)
- Many pieces of re-useable code (headers and libraries)
- Standard powerful text editors (vi, emacs)
- Standard toolchain for building binaries (e.g. autotools, make, gcc, ld, etc.)
- Standard support for scripting languages (perl, python, ruby, etc.)
Compiling
Source code can be compiled into binary following standard (optional) steps:
tar -xzf prog.tar.gz
cd prog
(autoconf)
(./configure)
make
sudo make install